张永勇与合作者在流域水循环系统模拟与径流情势影响评价方面取得进展
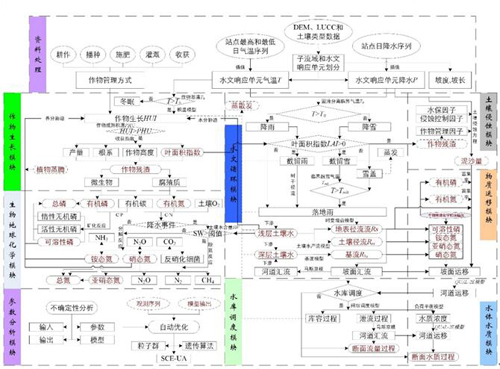
自全球水系统计划(Global Water System Project) 提出以来,水循环已逐渐被认为是联系流域诸多与水相关过程(水文过程、环境化学过程、生态过程和社会水循环等)的关键性纽带。传统水循环研究重点关注单一要素或单一过程,忽视了水循环多过程的相互作用机制,存在一定局限性和不确定性。中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所张永勇副研究员与合作者在国家自然科学基金(41271005)、中科院青年创新促进会、中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所秉维优秀青年人才计划(2015RC201)和国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2012CB955304)等支持下,在水循环多过程耦合均衡模拟、径流多要素模拟和影响评价等方面取得了如下进展:
 |
|
水循环系统模型框图 |
相关成果列表:
1. Zhang YY, Shao QX, Ye AZ, Xing HT and Xia J. Integrated water system simulation by considering hydrological and biogeochemical processes: model development, with parameter sensitivity and autocalibration. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2016, 20:529–553.
2. Zhang YY, Zhou YJ, Shao QX, Liu HB, Lei QL, Zhai XY and Wang XL. Diffuse nutrient losses and the impact factors determining their regional differences in four catchments from North to South China. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 543:577-594.
3. Zhang YY, Shao QX and Taylor JA. A balanced calibration of water quantity and quality by multi-objective optimization for integrated water system model. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 538:802-816.
4. Zhang YY, Shao QX, Zhang SF, Zhai XY and She DX. Multi-metric calibration of hydrological model to capture overall flow regimes. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 539:525-538.
5. Zhang YY, Zhai XY, Shao QX and Yan ZQ. Assessing temporal and spatial flow regime alterations in the regulated Huai River Basin, China. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 529:384-397.
6. Zhang YY, Fu GB, Sun BY, Zhang SF and Men BH. Simulation and classification of the impacts of projected climate change on flow regimes in the arid Hexi Corridor of Northwest China, Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmosphere, 2015, 120, 7429-7453.
7. 张永勇. 复杂流域水系统模型系统.登记号:2016SR040307.
8. 张永勇. 流域水系统模型参数分析软件.登记号:2016SR039945.
9. 张永勇. 水库入流预报系统.登记号: 2016SR148971.
10. 张永勇,高扬,夏军 等. 流域水-生物地球化学循环及其耦合均衡模拟. 被评为2016年度中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所年度十大研究进展.
附件下载: